sharks tooth guide
Shark teeth are fascinating fossils that reveal insights into shark evolution and marine ecosystems. Their shapes, sizes, and textures vary, reflecting diverse diets and survival strategies. Sharks continually shed teeth, with some species losing thousands in a lifetime. These teeth, often found on beaches and in rivers, serve as natural history treasures, helping us understand these apex predators’ adaptability and enduring presence in oceans worldwide.
What Are Shark Teeth?
Shark teeth are hard, calcified structures used by sharks for catching and eating prey. Designed for specific diets, they vary in shape, size, and texture, from triangular and serrated to flat and needle-like. Composed of hard tissues, these teeth are highly durable, often surviving for millions of years as fossils. Found in oceans, rivers, and even landlocked areas, they provide a glimpse into the evolutionary history of these marine predators and their adaptability to diverse environments.
Why Are Shark Teeth Important?
Shark teeth are vital for understanding shark evolution, diet, and ecological roles. They provide clues about ancient marine ecosystems and species diversity. Fossilized teeth help paleontologists study extinct species, like the massive Megalodon. Additionally, they aid in conservation efforts by offering insights into shark behavior and population dynamics. As natural history artifacts, shark teeth also inspire scientific curiosity and educational initiatives, making them invaluable tools for research and public engagement in marine biology.
The History of Shark Teeth Fossils
Shark teeth fossils hold significant historical value, offering insights into ancient marine life and shark evolution. These fossils, spanning millions of years, reveal how sharks adapted to changing environments. Fossilized teeth from species like Megalodon highlight the diversity of prehistoric sharks. They provide critical evidence for studying extinct species, ecosystem dynamics, and evolutionary adaptations, making them invaluable for paleontological research and understanding the Earth’s marine history.
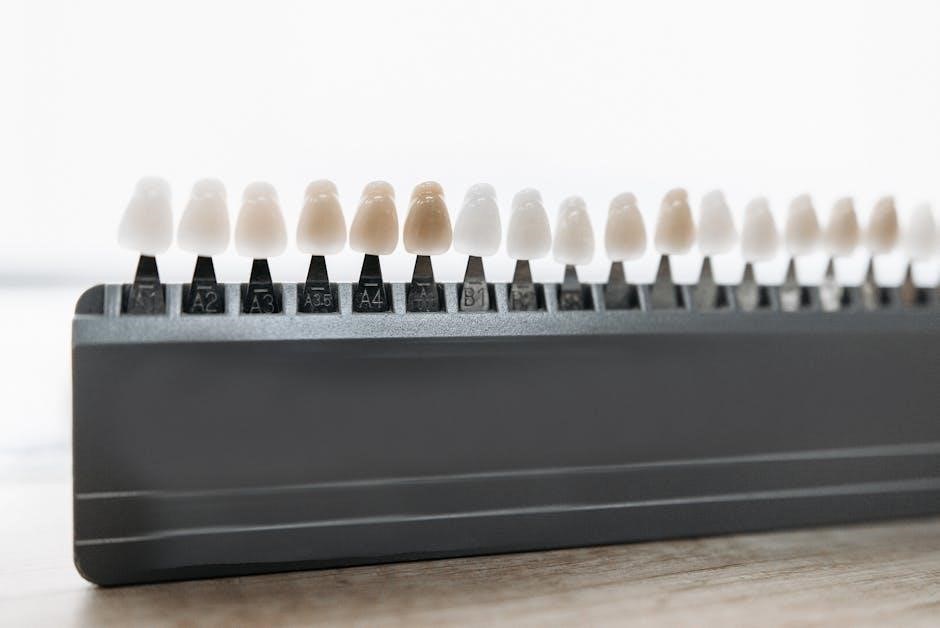

Anatomy of Shark Teeth
Shark teeth consist of a crown, root, and enamel coating. Their shape and serrations vary, aiding in cutting, crushing, or gripping prey efficiently for survival.
Structure of a Shark Tooth
A shark tooth’s structure includes a crown, root, and enamel coating. The crown is the visible part, varying in shape and serration depending on species and diet. The root anchors the tooth in the jaw, while the enamel provides hardness and durability. This design allows teeth to perform specific functions, such as cutting, crushing, or gripping prey, making them highly efficient tools for hunting and survival.
Differences Between Modern and Fossilized Teeth
Fossilized shark teeth are mineralized, hardened, and often darker in color, while modern teeth retain their natural white or off-white hue. Fossilized teeth may lack roots due to erosion, whereas modern teeth typically have intact roots. Over time, fossilization replaces organic material with minerals, making fossilized teeth more durable. Modern teeth, however, are lighter and more prone to wear, reflecting their recent origin and functional use in sharks’ jaws.
Root Structure and Its Significance
The root structure of shark teeth anchors them securely in the jaw, enabling efficient biting and gripping. Modern teeth typically have intact roots, while fossilized ones may lose them due to erosion. The root’s design allows for smooth tooth replacement, a critical adaptation for sharks’ continuous feeding needs. This structure also provides insights into evolutionary adaptations, as different species exhibit variations in root complexity to suit their dietary requirements.
Shark Teeth Identification
Shark teeth identification involves analyzing size, shape, texture, and root structure. These traits help distinguish species like Great Whites, Tigers, and Bulls, making each tooth unique.
Key Characteristics for Identification
Key characteristics for identifying shark teeth include shape, size, texture, color, and root structure. Serrated edges, triangular shapes, and distinctive roots help distinguish species like Great Whites or Tigers. Texture varies from smooth to coarse, while colors range from white to black. Using magnifying tools and reference guides aids in detailed examinations, ensuring accurate species identification.
Common Shapes and Sizes of Shark Teeth
Shark teeth vary widely in shape and size, reflecting their function. Triangular, serrated teeth are typical of predators like Great Whites, designed for piercing flesh. Broad, flat teeth are found in species that crush shells, while needle-like shapes are common in fish-eaters. Sizes range from tiny, millimeter-long fragments to massive Megalodon teeth exceeding 7 inches. These variations provide clues about the shark’s diet and ecological role.
Texture and Color Variations
Shark teeth exhibit diverse textures and colors, influenced by age and species. Fossilized teeth often appear black, brown, or gray due to mineralization, while modern teeth are typically white or pearly. Some species, like the Tiger Shark, have coarse, serrated textures, while others, such as the Nurse Shark, feature smooth surfaces. Color variations can indicate the tooth’s origin or condition, aiding in identification and providing insights into the shark’s biology and environment.

Tools for Shark Tooth Identification
Essential tools include magnifying glasses for detail, reference books for species comparison, and online guides for visual matching. Dichotomous keys aid systematic identification, while toothbrushes and scales help in cleaning and measuring specimens, ensuring accurate analysis and classification.
Essential Tools for Fossil Hunters
Fossil hunters rely on magnifying glasses to examine tooth details like serrations and root structures. Reference books and online guides provide species comparisons, aiding accurate identification. A sturdy sifting tray or fine-mesh sieve helps uncover small teeth in sediment. A soft-bristle toothbrush is ideal for gently cleaning fossils, while a small scale or ruler measures size. These tools enhance efficiency and precision in shark tooth hunting and preservation.
Digital Resources and Guides
Digital tools like OCEARCH’s shark tooth guide offer detailed insights into species-specific traits, aiding enthusiasts in identifying teeth. Mobile apps provide interactive databases for comparing finds; Online forums and communities allow collectors to share knowledge and seek expert advice. Websites with high-quality images and dichotomous keys simplify identification. These resources empower both novices and experienced hunters to enhance their understanding and refine their collecting techniques effectively.
Dichotomous Keys for Species Identification
Dichotomous keys are systematic tools for identifying shark teeth by presenting a series of choices based on physical characteristics. They guide users through decisions about tooth shape, size, serration, and root structure. These keys help narrow down species by eliminating options, ensuring accurate identification. While digital versions exist, physical guides remain essential for hands-on learning, offering detailed comparisons and visual aids to enhance the identification process for both novices and experts.

Species-Specific Shark Teeth
Each shark species has unique teeth adapted to its diet and survival needs. Teeth shapes and sizes vary, offering insights into their ecological roles and evolutionary adaptations.
Great White Shark Teeth
Great White Shark teeth are serrated, razor-sharp, and triangular, designed for grabbing and slicing through large prey like marine mammals and fish. Their robust structure and distinctive shape make them highly sought after by collectors. These teeth are a testament to the Great White’s apex predator status, offering insights into its feeding habits and evolutionary success. Their fossilized forms remain popular among enthusiasts, showcasing their historical and ecological significance.
Tiger Shark Teeth
Tiger Shark teeth are curved with a unique “can-opener” shape, aiding in gripping and sawing through tough prey like sea turtles. Their teeth are versatile, adapted for both crushing and piercing, reflecting their diverse diet. The distinctive curvature and serrations make them easily identifiable. Tiger Shark teeth are highly valued by collectors for their rarity and evolutionary significance, offering insights into the species’ adaptability as apex predators in various marine environments.
Bull Shark Teeth
Bull Shark teeth are broad and flat, with a distinctive saw-like structure, ideal for crushing hard-shelled prey. Their serrated edges aid in gripping and tearing flesh, reflecting their robust diet. These teeth are highly adaptable, suited for both marine and freshwater environments. Bull Sharks’ teeth are a testament to their versatility as apex predators, capable of thriving in diverse ecological settings and preying on a wide variety of species, from fish to mammals.
Nurse Shark Teeth
Nurse Shark teeth are small and serrated, designed for crushing hard-shelled prey like clams and crustaceans. Their mouth contains multiple rows of these specialized teeth, enabling efficient grinding. The triangular shape and rough texture of Nurse Shark teeth make them distinct, reflecting their bottom-dwelling, ambush predator lifestyle. These teeth are a key adaptation to their diet and environment, showcasing their evolutionary specialization for navigating and feeding on tough, armored prey effectively.
Sand Tiger Shark Teeth
Sand Tiger Shark teeth are sharp and arranged in three rows that protrude in all directions, aiding in catching and holding prey. Their distinctive teeth are well-suited for their diet of small fish, squid, and crustaceans. This arrangement enhances their ability to grasp and retain struggling prey, making them efficient hunters in their marine habitats.
Bluntnose Sixgill Shark Teeth
Bluntnose Sixgill Shark teeth are broad and saw-like, with a distinctive shape that allows for efficient cutting and tearing of prey. Found in both the upper and lower jaws, these teeth are designed to saw back and forth, making them ideal for larger prey. The lower jaw features broader, more serrated teeth, while the upper jaw has narrower ones. Their triangular shape and serrated edges make them highly sought after by collectors for their unique appearance and functionality.

Conservation and Legal Considerations
Shark tooth collecting must be done ethically to preserve marine ecosystems. Legal restrictions often apply to protect endangered species and their habitats. Always adhere to local regulations.
Importance of Ethical Collecting
Ethical collecting ensures the preservation of marine ecosystems and shark populations. Collectors should avoid removing teeth from protected species or sensitive habitats. Following local regulations and respecting protected areas helps maintain biodiversity. Avoiding over-collection and minimizing environmental impact are key. By collecting responsibly, enthusiasts contribute to conservation efforts and promote a sustainable future for these marine treasures.
Legal Restrictions on Shark Tooth Collection
Legal restrictions on shark tooth collection vary by region and species. Many areas prohibit collecting teeth from endangered species to protect vulnerable populations. Permits may be required for certain locations, and some sites, like national parks, have strict no-collection policies. Additionally, commercial collection often faces tighter regulations than recreational gathering. Ensuring compliance with local laws helps preserve shark populations and maintains ecological balance.
Role of Conservation in Shark Tooth Research
Conservation plays a vital role in shark tooth research by ensuring the preservation of these fossils for scientific study. Efforts focus on protecting habitats where teeth are found, preventing over-collection, and promoting sustainable practices. Research on shark teeth provides insights into species evolution, diet, and ecosystem health, aiding in broader marine conservation initiatives; Ethical collecting practices support both scientific advancement and the protection of shark populations for future generations.
Collecting Shark Teeth
Shark teeth can be found on beaches, in rivers, and even landlocked areas. The best spots include Venice Beach, Florida, known as the Shark Tooth Capital. Techniques like sieving sand, using sifting tools, and scanning wet sand edges are effective. Equipment such as mesh screens and small brushes aids in discovering these fossils, making the hunt a rewarding experience for enthusiasts and researchers alike.
Best Locations for Shark Tooth Hunting
Shark teeth are commonly found on beaches, particularly in areas with shallow waters and abundant marine life. Venice Beach, Florida, is renowned as the “Shark Tooth Capital of the World.” Coastal regions like North Carolina, especially near Wilmington, are also rich in fossilized teeth. Rivers and creek beds, such as those in the Chesapeake Bay region, offer additional opportunities. Beaches with ancient sea beds exposed, like parts of California and South Carolina, are prime hunting spots for these fossils.
Techniques for Finding Shark Teeth
Shark tooth hunting is easiest in shallow waters where teeth are more likely to wash ashore. Walk along the beach at low tide, scanning the sand for triangular shapes. Use a small sifting tool or sand scoop to search through shells and pebbles. Focus on areas with erosion or shell beds, as these often yield fossils. Patience and sharp eyesight are key to spotting these hidden treasures.
Equipment Needed for Shark Tooth Collecting
Essential tools for shark tooth collecting include a sand sifter, gloves, and a magnifying glass. A small shovel or trowel can help dig in sandy areas, while a mesh screen aids in filtering sediment. Waterproof bags or containers are useful for storing finds. Wearing sturdy shoes and protective clothing is recommended for comfort during long hunts. Optional items like snorkeling gear can expand your search to shallow waters.

Preserving and Displaying Shark Teeth
Proper preservation involves gentle cleaning and protective coating. Display options include shadow boxes, jewelry, or storage cases, showcasing your finds while maintaining their condition.
Methods for Cleaning and Preserving Teeth
Shark teeth should be cleaned gently with mild detergents to avoid damage. Soaking in water or using soft brushes can remove dirt. After cleaning, apply a protective coating like varnish to prevent erosion. Store teeth in dry, cool environments to maintain longevity. For fossilized teeth, professional conservation methods may be necessary to ensure stability and preservation for future study and display.
Creative Ways to Display Shark Teeth
Shark teeth can be creatively displayed in shadow boxes, necklaces, or keychains. For a unique showcase, arrange teeth in framed collages or resin art. Embedding them in clear acrylic or epoxy preserves and highlights their natural beauty. DIY jewelry-making allows for personalized wearables, while decorative bowls or glass jars offer elegant storage. These methods not only protect the teeth but also transform them into striking conversation pieces that celebrate marine history and personal collecting adventures.
Storing Shark Teeth for Longevity
To preserve shark teeth, store them in airtight containers to protect against moisture and dust. Separate each tooth to prevent scratching. Place them in soft material like foam or fabric for added cushioning. Maintain a stable humidity and temperature environment to avoid warping or cracking. Avoid exposure to harsh chemicals or extreme temperatures. Handle teeth gently to prevent damage. Proper storage ensures your collection remains intact and retains its value for years to come.

Shark Tooth Hunting Locations
Shark teeth are often found on beaches, particularly in areas like Venice Beach, Florida, known as the Shark Tooth Capital of the World; Rivers and creek beds also yield fossils, while landlocked regions with ancient oceanic histories can harbor hidden treasures, making them prime spots for enthusiasts seeking these prehistoric relics.
Beaches Known for Shark Teeth
Beaches are premier locations for shark tooth hunting, with Venice Beach, Florida, famously dubbed the Shark Tooth Capital of the World. Other notable spots include Sarasota County beaches and the Gulf Coast, where fossil-rich sands yield ancient treasures. Beachcombers often find teeth along the water’s edge or in shallow tide pools. Low tide and post-storm conditions are ideal for searching, as waves uncover hidden fossils. Using a sifter or fine-mesh screen can enhance discovery, making beach hunting a rewarding experience for collectors of all levels.
Rivers and Creek Beds as Hunting Spots
Rivers and creek beds are rich hunting grounds for shark teeth, as flowing water often concentrates fossils in gravelly areas. Locations like the Chesapeake Bay and Cooper River are known for yielding teeth. Using a small screen or sieve can help sift through sediment and uncover hidden treasures. Searching after storms or floods can be particularly rewarding, as these events often expose new fossils. These freshwater spots offer a unique opportunity to discover shark teeth in unexpected places.
Landlocked Areas for Fossilized Teeth
Landlocked areas, once ancient seabeds, also yield fossilized shark teeth. Regions like the Chesapeake Bay and Badlands were submerged millions of years ago, leaving behind teeth embedded in sediment. These areas are now dry land but rich in fossils. Hunters often find teeth in gravel pits, riverbanks, and even farmland. Expert tips suggest consulting geological maps and joining fossil-hunting clubs to locate these hidden treasures, providing a unique glimpse into prehistoric marine life far from modern oceans.

Advanced Topics in Shark Tooth Research
Shark teeth reveal evolutionary insights and ecological roles, aiding paleontological studies. Rare teeth hold economic value, while advanced research explores their microscopic structures and ancient species connections.
The Role of Shark Teeth in Paleontology
Shark teeth are vital fossils in paleontology, providing insights into ancient marine ecosystems and evolutionary history. Their durable enamel and unique shapes help date geological periods and reconstruct predator-prey dynamics. By analyzing tooth structure, scientists infer dietary habits and environmental conditions. Fossilized teeth also reveal species distribution and extinction events, such as the presence of Megalodon, offering a window into the past that shapes our understanding of oceanic life and biodiversity over millions of years.
Evolutionary Insights from Shark Teeth
Shark teeth offer remarkable evolutionary insights, revealing how species adapted to changing environments and prey over millions of years. Their shapes and structures indicate dietary specializations, from serrated Great White teeth for slicing flesh to Tiger Sharks’ curved teeth for crushing hard-shelled prey. These adaptations highlight evolutionary pressures, while fossil records like Megalodon’s massive teeth demonstrate how apex predators rose and fell, shaping marine biodiversity and ecological balance across geological time scales.
Economic Value of Rare Shark Teeth
Rare shark teeth, particularly fossilized ones like Megalodon, hold significant economic value, sought after by collectors and researchers. Their rarity, size, and condition drive demand, with some fossils fetching thousands. The market for these teeth supports eco-tourism and paleontological research, while also fostering a vibrant collector community that preserves and studies these ancient relics, blending historical significance with financial worth in a unique intersection of science and commerce.
Shark teeth collecting offers a rewarding journey into marine history, fostering curiosity and conservation. As interest grows, future explorations will uncover more secrets about these ancient treasures.
Final Thoughts on Shark Tooth Collecting
Shark tooth collecting is a captivating hobby that combines adventure, education, and environmental appreciation. It fosters a deeper connection with marine life and history. For many, the thrill lies not only in the hunt but also in the stories each tooth tells. Ethical practices ensure sustainability, while shared knowledge strengthens communities. Whether for personal joy or scientific contribution, shark tooth collecting continues to inspire curiosity and conservation efforts globally.
The Future of Shark Tooth Research
The future of shark tooth research lies in advancing technologies and collaborative efforts. Digital databases and AI-driven identification tools will enhance species recognition; Conservation-focused studies will uncover more about shark evolution and ecological roles. Public engagement through educational programs will foster a deeper appreciation for these fossils, ensuring sustainable practices and continued discovery. As research evolves, it will bridge gaps between science, education, and conservation, inspiring future generations to explore and protect marine life.

Additional Resources
Explore recommended books like Fossil Sharks of the Chesapeake Bay and online guides for detailed shark tooth identification. Join forums and communities for expert tips and shared discoveries, enhancing your knowledge and collecting journey with reliable resources and insights from seasoned collectors and researchers.
Recommended Books and Guides
For in-depth knowledge, explore books like Fossil Sharks of the Chesapeake Bay by Bretton Kent, offering detailed species insights. A Beachcomber’s Guide to Fossils by Ashby Gale provides practical tips for collectors. Online resources like OCEARCH and Sharkier.com offer comprehensive guides, while forums and communities share expert advice. These resources enrich your understanding and collecting experience, blending scientific detail with hands-on expertise for enthusiasts and researchers alike.
Online Communities and Forums
Join online forums like Facebook groups such as Shark Tooth Enthusiasts and Reddit’s r/sharkteeth to connect with fellow collectors. Websites like Sharkier.com and OCEARCH offer valuable resources, including identification guides and expert tips. These platforms allow enthusiasts to share findings, seek advice, and learn from experienced collectors, fostering a vibrant community dedicated to shark tooth exploration and discovery.
Expert Tips for Beginner Collectors
Start with basic tools like a sifter and gloves. Search in shallow waters and along beach edges. Look for dark triangular shapes. Join online forums for identification help. Practice patience and persistence. Store finds in a dry, cool place to preserve them. Consider guided tours for hands-on experience. Always follow local regulations to ensure ethical collecting. These tips will enhance your shark tooth hunting journey and help you build a valuable collection over time.



Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.